All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents

Interact these problems to relevant job groups, follow with till there's a remedy, and report the consumer resolution. Make sure that all jobs are following their spending plans and distribution times.
Establish a system to plan, track, and record every solitary program you manage. At least 4-6 years of experience in program administration with IT tasks is critical.
Technology is nitty-gritty when it comes to the innovation sector, and within that standard, there's a behind the curtain orchestrator making sure whatever runs seamlesslythe Technical Program Supervisor (TPM). This unsung hero plays a pivotal duty in the success of technology jobs, bringing order to turmoil and ensuring that the equipments of growth turn smoothly.
What certifications are recommended for a Program Management Certification For Tech career?
It's a delicate dancing between establishing ambitious objectives and guaranteeing expectations remain firmly based actually - google technical program manager interview. technical program management. Yet it's not nearly developing a strategy; it has to do with implementing it faultlessly. TPMs wear the hats of both visionary planners and pragmatic executors, making certain that every step aligns with the overarching job objectives

In the large landscape of tech jobs, efficient interaction is the bridge that attaches disparate groups and stakeholders. Right here, TPMs shine as experienced translators, decoding the complex language of technology for non-technical stakeholders. They bridge the gap, ensuring that everyone, no matter of their technical history, comprehends the project's goals and progress.
They have the foresight to recognize possible mistakes, varying from unforeseen technical challenges to exterior variables past the team's control. TPMs establish methods to alleviate dangers, making sure that the job sails through stormy weather condition with durability.
Below, TPMs take on the duty of allocators-in-chief, strategically distributing sources to enhance efficiency. As the task landscape shifts, TPMs reallocate sources dynamically, ensuring that the team remains agile and receptive.
How do I get started as a Technical Program Manager Roles At Faang?
TPMs, in this respect, become the gatekeepers of excellence. They established rigid requirements for every part of the job, from code to layout, ensuring that the end product satisfies or exceeds the defined requirements.
TPMs produce a culture where excellence is not just a goal yet a behavior, penetrating every facet of the task. Via their meticulous oversight, they impart confidence in stakeholders and contribute to the lasting success and reputation of the organization. Being a successful TPM calls for greater than simply a propensity for project administration.
What are the essential skills for a Technical Program Manager Resume Tips at Google?
While TPMs may not be coding wizards, they need a strong understanding of the technological landscape. This consists of knowledge with the modern technologies included, a recognition of industry patterns, and the ability to understand the ramifications of technical decisions. Leading without authority is a TPM's superpower. They have to motivate and lead groups made up of people from various departments, each with their very own goals and priorities.
TPMs are the interaction nexus of a task. Whether it's communicating complicated technological information to a non-technical target market or promoting cooperation among group participants, effective interaction is non-negotiable.
As innovation progresses, so does the role of the TPM. Agile has become much more than simply a buzzword; it's a method of life for numerous TPMs.
, has become a cornerstone in the TPM's toolkit. In the age of large data, TPMs are increasingly counting on data-driven understandings to educate their decision-making procedures.
What does the hiring process for a Amazon Technical Program Manager look like?
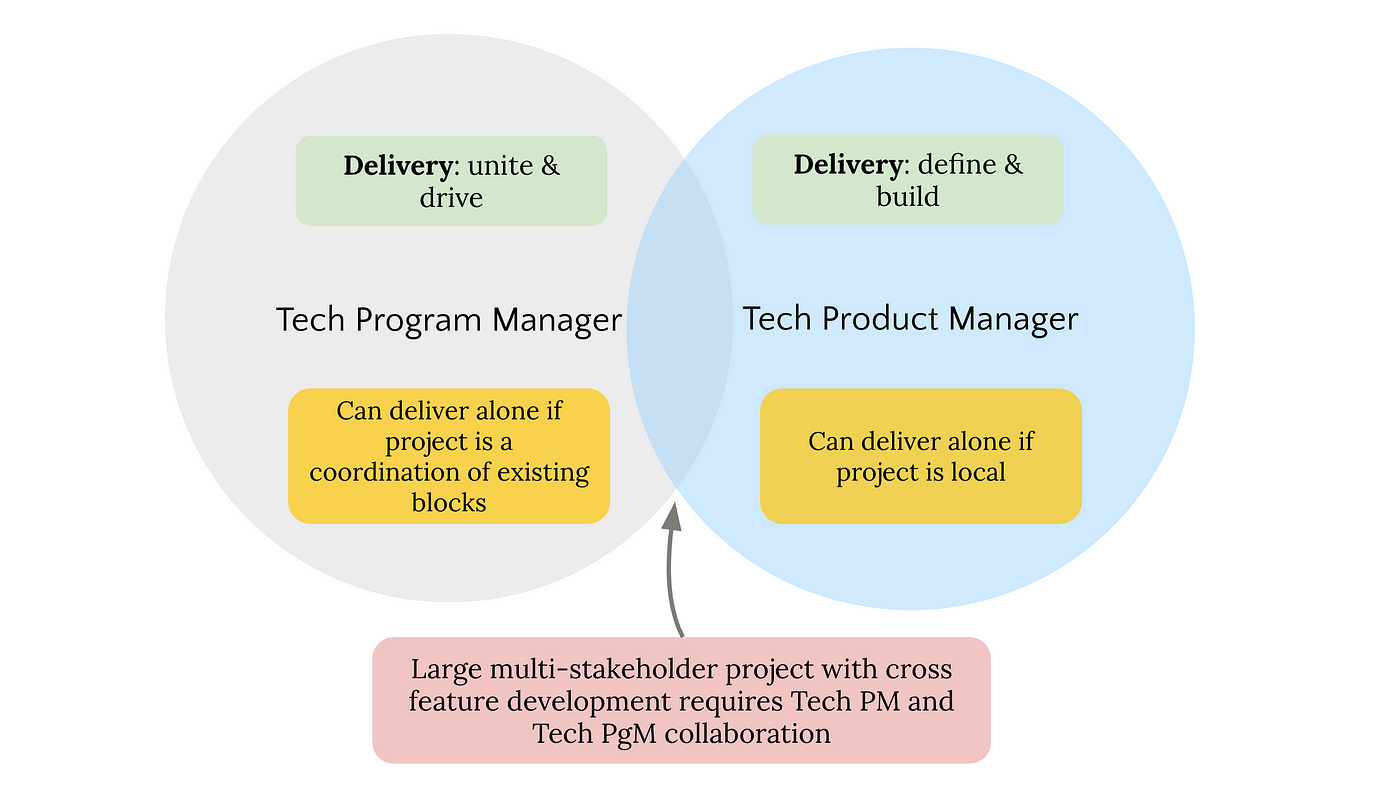
Unlike typical project managers, TPMs have to deeply comprehend the technological elements of the tasks they handle. This twin know-how allows them to interact with design teams effectively, recognize technical obstacles, and make sure that jobs are completed promptly and within budget. Whether you're wanting to hire a TPM or end up being one, recognizing the duties and skill collections required is vital for success in the technology sector.
The courses cover crucial subjects such as job lifecycle administration, danger assessment, source appropriation, and software growth processes. With an emphasis on real-world applications, our training guarantees you are prepared to handle the complexities of technical projects in any kind of market. Gaining a qualification can significantly boost your job potential customers, showing to employers that you have the knowledge and abilities required to prosper in a TPM role.
From start-ups to Fortune 500 firms, companies throughout the world are seeking certified specialists to lead their technical programs. Whether you're seeking to hire a TPM or are interested in TPM work, TPM Institute can assist you navigate the work market and connect you with the ideal possibilities. Our training courses are not nearly finding out; they are concerning releasing your job in among the most popular fields in the tech sector.
Our are devoted to supplying you with the best possible education and learning, using understandings grounded in real-world experience. They are committed to assisting you attain your certification and be successful in your profession. For even more details about our programs and certifications, at Take the following action in your occupation with TPM Institute and become a leader in technological program management.
What does a Tpm Career Growth do?
There's a tendency for people to be attracted toward extremes when conceiving technical program managers. The reality is there is a spectrum of technological deepness amongst TPMs, and this often differs by task and client.
They can express complicated technological concepts to non-technical stakeholders and assist in cooperation in between diverse teams. TPMs excel at identifying and dealing with issues that emerge during project implementation, guaranteeing that jobs remain on routine and within budget. They inspire and direct their groups, promoting cooperation, technology, and continual improvement. TPMs' obligations can vary depending on the company and the certain job they're servicing.
TPMs work to make sure that all employee are functioning in the direction of the same purposes, protecting against miscommunication and wasted initiative. They anticipate and adjust to changes in task requirements, ensuring that tasks can pivot smoothly when required. TPMs proactively deal with possible problems, decreasing the likelihood of task delays and failures. They encourage their groups to try out brand-new ideas and technologies, driving continuous improvement and growth.
TPMs work to guarantee that all team members are working in the direction of the exact same objectives, protecting against miscommunication and squandered initiative. TPMs proactively deal with possible problems, lowering the chance of task delays and failings.
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
Software Developer (Sde) Interview & Placement Guide – How To Stand Out
The Ultimate Software Engineer Interview Prep Guide – 2025 Edition
The Science Of Interviewing Developers – A Data-driven Approach
More
Latest Posts
Software Developer (Sde) Interview & Placement Guide – How To Stand Out
The Ultimate Software Engineer Interview Prep Guide – 2025 Edition
The Science Of Interviewing Developers – A Data-driven Approach